
Neonatal cranial malformations are deformities of the growing skull caused by mechanical pressure on certain parts before, during, or after birth.
Normal growth is hindered if, for any reason, the skull experiences excessive or continuous pressure, leading to the flattening of a part of the skull.
There are 3 types of craniofacial deformities that may potentially occur in newborns:
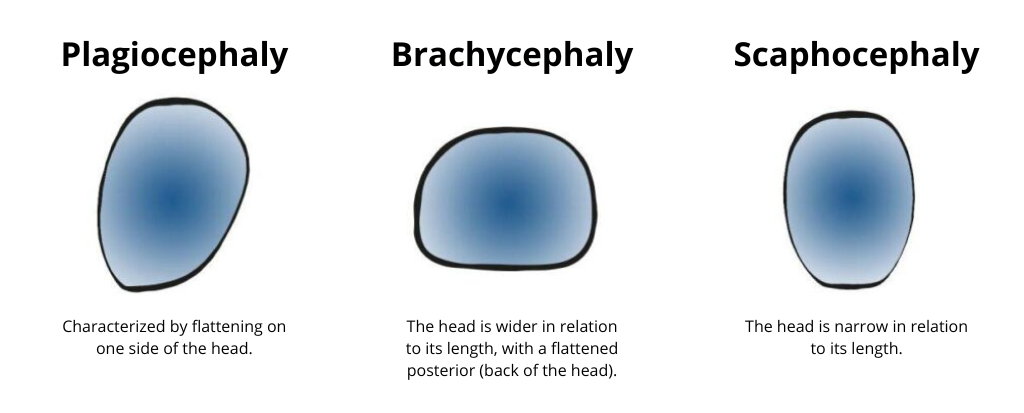
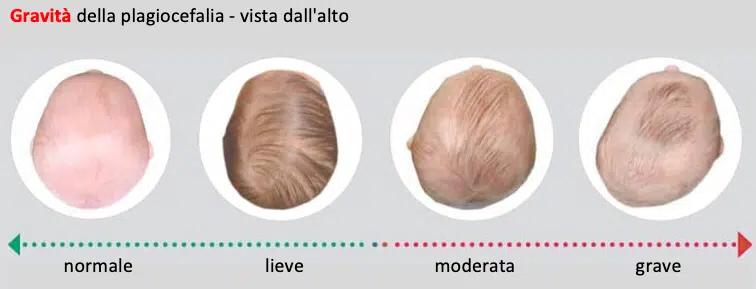
Plagiocephaly is one of the cranial abnormalities classified as "dysmorphisms." Specifically, it refers to the deformation of a newborn's head during the first months of life. Plagiocephaly is a cranial deformity characterized by the flattening of the back of the head, usually on the right side, which can be accompanied by a forward shift of the same side of the head.
The forehead on the flattened side may be more pronounced, the eye on the same side may be more open, and the ear may be positioned further forward compared to the other side.
Top view:
Side view
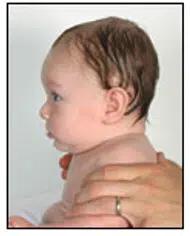
Front view
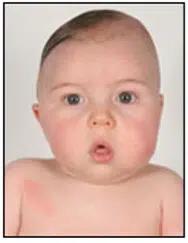
Bottom view:
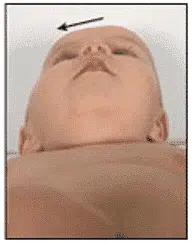
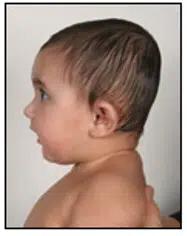
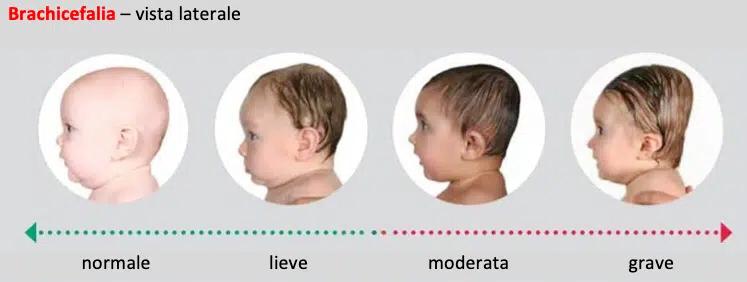
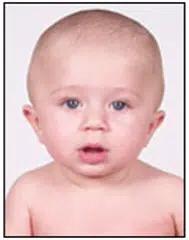
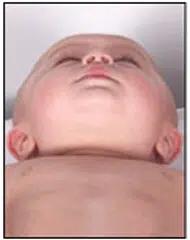
Positional Brachycephaly is a cranial deformity characterized by a more or less symmetrical flattening of the entire back of the head.
The heads of these children are shorter than normal and, to compensate, may appear wider when viewed from the front or taller when viewed from the side.
In some cases, it results in a virtually square-shaped head.
Top view:
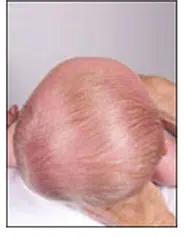
Side view
Front view
Bottom view:
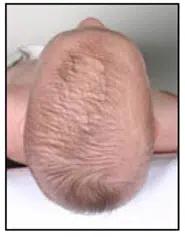
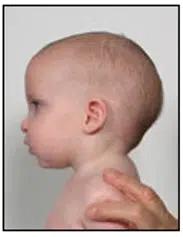
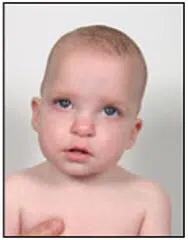
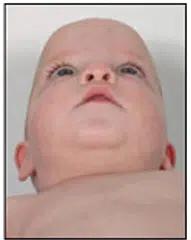
Scaphocephaly is a cranial deformity characterized by a narrow, tall, and elongated head due to transverse flattening and elongation in the anteroposterior direction.
It occurs more frequently in premature and former premature babies.
It also affects children who sleep with a flat head on their side (temporo-parietal region).
Scaphocephaly can be either positional or the result of craniosynostosis due to the premature fusion of the sagittal suture of the skull.
Top view:
Side view:
Front view
Bottom view:
Premature babies are more likely to suffer from scaphocephaly due to the relative macrocephaly they present and the lack of tone in the cervical musculature.

Venanzio Signorino D.O.
Corso Vittorio Emanuele, 203
Salerno (SA) – 84122
P.I. 04598220657
Tel: +39 328 00 44 190
e-mail:
info@osteopatiasalerno.it